Practical Approaches
Reducing Manufacturing Costs
Manufacturing costs include expenses for materials, labor and equipment. We’ll break down what these costs consist of and present measures to reduce them.
Manufacturing costs are the expenses incurred in the creation of goods and services. They mainly include costs for materials and labor, but also cover energy costs, equipment expenses, and facility-related costs.
Categories of manufacturing costs
Manufacturing costs can be divided into three categories:
1. Direct Material Costs
Direct material costs refer to the expenses for raw materials, auxiliary materials, consumables, components, semi-finished goods and intermediate products that can be directly assigned to a specific product.
In discrete manufacturing, direct material costs are typically defined in a bill of materials (BOM).
Examples: Screws, metal pipes, cotton, chips, processors, and pre-assembled engines
2. Direct Labor Costs
Direct labor costs are wages paid to employees that are directly involved in the production of goods or services. These costs are traceable to individual products, jobs or production batches.
Examples: Wages for machine operators (tracked per product), assembly wages for putting components together, and piece-rate wages (payment based on the number of units produced).
3. Manufacturing Overhead
Manufacturing overhead (also known as factory overhead) are all the indirect costs associated with the manufacturing process. It includes all costs that cannot be traced to specific products.
Examples:
- Indirect material costs (e.g. cleaning supplies, oils for machinery)
- Indirect labor costs (e.g. wages of supervisors, maintenance staff and warehouse workers)
- Factory-related costs (e.g. depreciation of equipment, factory rent, energy, insurance, security)
Cost Reduction
5 measures to lower manufacturing costs
Below, we present five practical approaches to reducing production costs across different areas:
1. Lowering material costs by minimizing waste
Rejects (also called waste or scrap) are products that fail to meet quality standards and therefore cannot be used or sold.
Despite being unusable, they still generate material and labor costs without contributing to a company’s revenue. Reducing the reject rate is therefore a key measure for cutting unnecessary material costs and often one of the main goals in production optimization.
One of the most important requirements for lowering the reject rate is comprehensive data collection and analysis. This includes information like production volumes, quality inspection results and manual reports from employees. This data provides insights into the root causes of scrap and forms the basis for targeted improvements.
Identifying and accessing relevant data sources, bringing data together in a meaningful way and analyzing it effectively are all critical steps in understanding and addressing the causes of scrap.
Example: Reducing waste with manubes
manubes is a cloud solution for manufacturers that integrates a variety of tools on a single platform. Users gain access to intuitive designers, enabling the development of custom applications in the areas production planning, production control and production monitoring.
Using industrial standard interfaces, manufacturers can integrate field devices and databases as well as different OT and IT systems with the platform. Data can be collected and organized in custom data models.
This allows manubes to collect scrap data from a wide range of sources on a single central platform. The data can be visualized in real-time dashboards, included in production reports or analyzed using the AI assistant.
On our page about the reject rate, we take a closer look at potential causes of scrap that can be identified using this approach.
We also cover measures to reduce the reject rate, including:
- Automated data entry to prevent errors
- Automated checks of materials and tools
- Digital work instructions
- Systematic documentation of maintenance activities
2. Lowering training expenses with digital work instructions
Training is essential in manufacturing – whether for onboarding new staff or introducing new technologies. Yet, traditional methods like seminars, workshops, and classroom-based courses (off-the-job training) can be costly and often lack practical relevance.
As a result, many companies are shifting toward hands-on learning (on-the-job training), often supported by tools like digital work instructions.
Digital work instructions are multimedia, interactive and context-sensitive resources that guide users through tasks or provide support in various ways. They’re typically accessible on mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, or wearables, making them available anytime and anywhere.
These instructions can offer a practical way to transfer knowledge while reducing the likelihood of errors. They can help ensure consistent execution of tasks and make existing knowledge easily accessible through visual guides, videos or checklists.
By utilizing digital work instructions, manufacturers can reduce material costs for printed training materials and minimize reliance on external training providers. Digitally supported on-the-job training also helps cut travel and seminar costs while enabling faster and more practical onboarding.
Digital work instructions can be continuously improved and refined based on user feedback.
Learn more about digital work instructions with manubes.
3. Reducing maintenance costs by optimizing your maintenance strategy
Equipment failures and unplanned downtime in production can lead to significant productivity losses. To prevent this, manufacturers invest in regular maintenance – especially in asset-intensive environments where maintenance represents a major cost factor.
Many digitalization initiatives aim to optimize equipment maintenance and address the inefficiencies of reactive maintenance strategies.
Instead of responding to breakdowns after they occur, modern approaches aim to analyze data to detect early signs of maintenance needs (predictive maintenance) or to improve future maintenance intervals (preventive maintenance).
Optimizing maintenance timing not only cuts costs by avoiding unnecessary maintenance but also helps prevent equipment failures by detecting signs of wear or malfunctions early on.
Additional ways to reduce maintenance costs include optimizing spare parts management (e.g. reducing inventory costs) and improving workforce and resource planning through digital tools.
Maintenance processes themselves can often be streamlined to save time and labor costs – for example, through mobile applications for documentation, data display and transmission.
4. Saving costs through automated reporting
Production reports summarize key metrics and results over specific time periods. In many companies, they serve as a critical basis for decision-making.
Alongside real-time data visualization, reports are an essential tool for achieving production transparency and supporting longer-term production monitoring.
However, creating and distributing reports can be time-consuming in practice, leading to significant labor costs. Digital reporting solutions can simplify this process through the use of templates and data integrations.
Example: Dynamic production reports with manubes
Our manubes platform provides access to reporting tools that enable the automated delivery of dynamic production reports.
manubes users can create custom report templates and link them to real-time data sources. Thanks to the platform’s integration capabilities, a wide range of machines and devices (e.g. PLCs), APIs, and software systems can be connected as data sources.
Reports can then be automatically generated as part of workflows. This allows them to be delivered through dedicated reporting hubs and portals, where end users can generate the reports they need on demand.
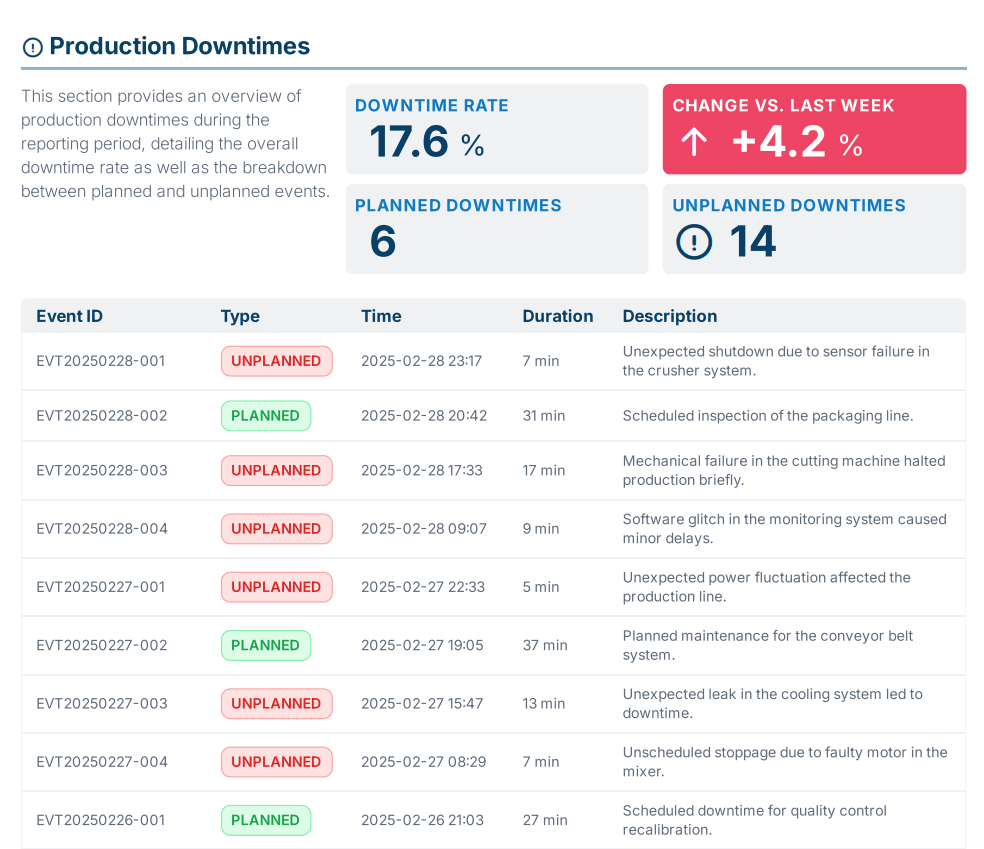
Report on downtimes during a reporting period
In practice, reporting with manubes leads to significant time and cost savings. In addition to reporting tools, companies gain access to a wide range of features for data management, data visualization, and app development – all within a single, centralized platform.
5. Saving costs through shorter cycle times
Cycle time is the total time it takes for a product to move through the entire production process. It includes processing times at each station as well as transport times, waiting periods between workstations, quality inspections, and delays caused by disruptions.
Reducing cycle time is one of the main goals of production management. Shorter cycle times achieved through more efficient processes can generate cost savings in several areas: Less unnecessary energy costs from idle time, reduced capital tied up in work-in-progress inventory and lower logistics, transport and labor costs.
In practice, waiting and idle periods – when a product is simply waiting to be processed – can make up a large portion of cycle lead time. Below are some strategies for reducing these time segments.
Example: Measures to reduce waiting times
Adjustment of batch sizes
With smaller batches, finished parts reach the next station more quickly. With larger batches, downstream stations may have to wait until a larger number of products are completed before they can continue.
Optimizing job sequencing
Companies can reduce setup and preparation times by scheduling consecutive jobs that use the same machine setups, tools and materials.
Asset Tracking
Manufacturers can track the location of materials or tools to avoid time losses and reduce travel distances for workers.
In-process inspections
Quality checks can be performed directly at the machine to reduce the number of downstream process steps.
Optimizing communication
Real-time information sharing allows employees at different stations to view the current status on mobile devices and receive instructions for the next work step.

Optimize your production with manubes
manubes offers a central platform for production data management, data visualization and workflow-based process automation.
Manufacturers gain access to a variety of innovative tools in order to quickly develop their own applications – tailored to their requirements.
Try manubes for free
Test the different manubes features in your personal cloud environment.
