Definition, Tasks and Useful Tools
Production Control
Production control is a core function within production management that includes the real-time management and successful execution of manufacturing plans. It ensures that products meet quality standards, deadlines and budget targets. In this article, we are going to explore the meaning, tasks, goals and tools of production control in more detail.
Definition
What is production control?
Production control is an important part of production management and can be seen as the operational “ground control” of the manufacturing process. It has three key aspects, explained in more detail below:
- Detailed planning and coordination
- Process monitoring and control
- Troubleshooting and adaptation
Detailed planning and coordination: Production control takes broader production plans and translates them into sequences of manufacturing steps, including timing and the allocation of machines, materials, and the right personnel.
Process monitoring and control: Effective production control systems are able to continuously gather and analyze data from the shop floor. This real-time monitoring allows companies to track progress, recognize potential bottlenecks, and identify any deviations from the plan. This lets a control team make proactive adjustments to optimize the output and prevent various issues from occuring.
Troubleshooting and adaptation: When unexpected issues arise (machine breakdowns, material delays, quality problems, …) the production control team makes adjustments in order to minimize disruption and keep the overall manufacturing process on track. This can include changes to the previously defined schedules, allocations etc.
Production control teams often work with specific metrics or KPIs that measure aspects such as equipment performance or product quality. You can find an overview here: Important metrics and KPIs for production
Tasks
Common tasks in production control
In practice, production control teams are responsible for several key tasks:
- Scheduling
- Dispatching
- Monitoring
- Troubleshooting
- Reporting
Scheduling: As a first step, production control teams create detailed production schedules that break down the manufacturing process into specific tasks and try to assign the available resources in the most optimal way. These schedules need to account for factors such as machine capacity and availability of personnel.
Dispatching: In the second step, production schedules are put into practice: The responsible employees initiate the production at each stage while following the pre-defined schedule. This includes issuing work orders, releasing materials from inventory, and providing the necessary instructions to workers and machine operators.
Monitoring: Once a process is running, production control is responsible for tracking the progress. Systems collect data on machine utilization, output rates, quality metrics, and resource consumption. This not only enables the team to spot potential issues early but also identify potential for optimizations (small-scale or large-scale).
Troubleshooting: In a complex manufacturing environment, unforeseen issues can be heavily minimized but not completely avoided. Proactively diagnosing and addressing problems like machine breakdowns, material shortages, or quality deviations is an important part of production control. The solution to such problems might involve re-routing work, expediting orders, or coordinating with maintenance teams.
Reporting: Last but not least, production control teams provide management with regular reports on production progress and various KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) such as capacity utilization, and efficiency metrics. The main goal is to enable data-driven decisions.
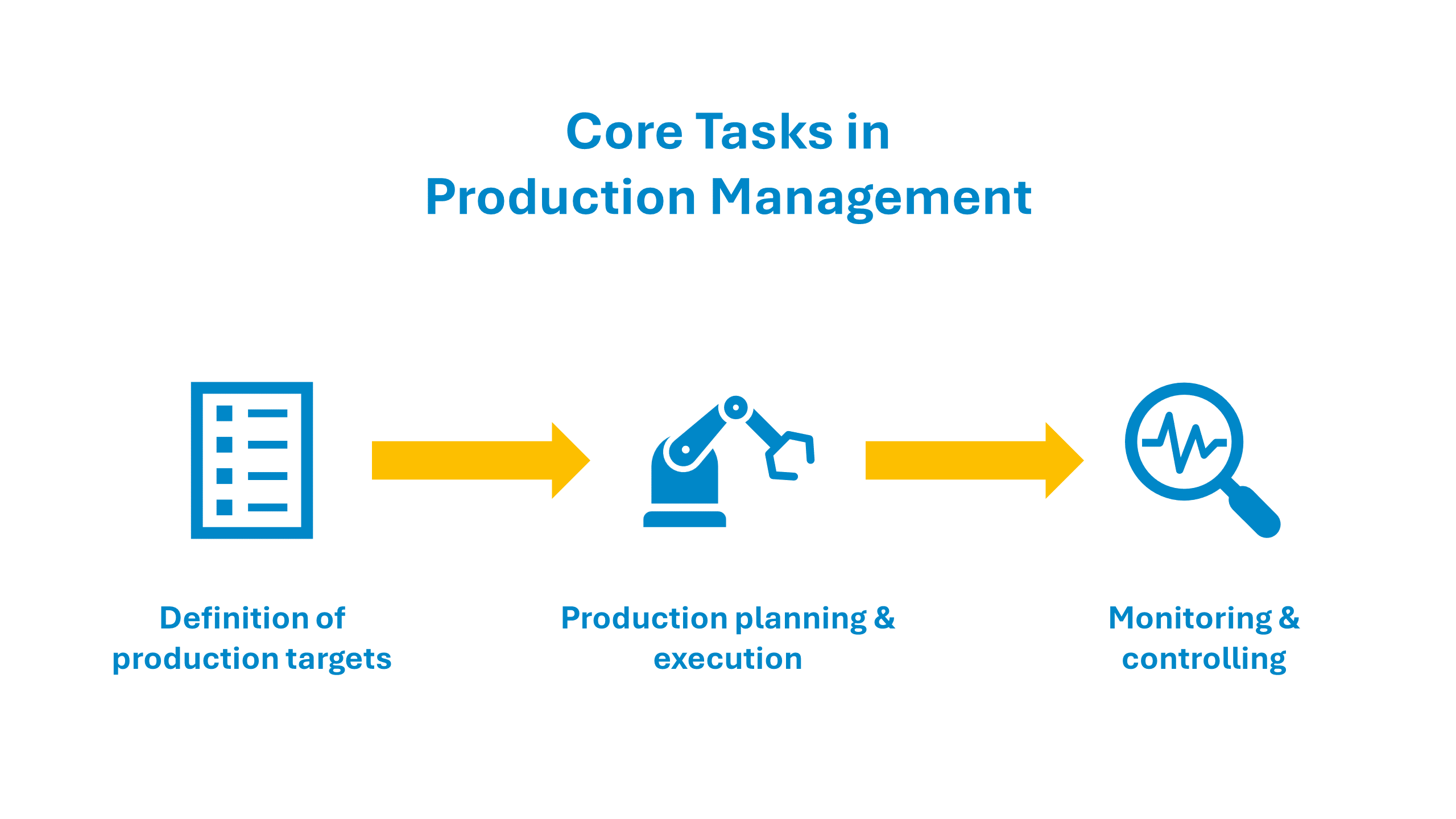
As mentioned in the introduction, production control is a large part of the broader production management, also referred to as „operations management“. The image below shows the main aspects of production management. After reading about the tasks above, you might notice how production control is heavily involved in the second and third step.

Digital production management in the cloud
With manubes, you are able to systematically automate production processes and visualize all areas of a production in real time.
The manubes platform offers worldwide access via web browser, easy operation and maximum security for production data.
Goals
What are the goals of production control?
Effective production control translates directly into the success of a manufacturing company. It aims to create optimized schedules, deal with issues affecting production (ideally before they even occur) and tries to gain insights from various types of production data.
Aside from the broader objective of optimizing production efficiency, there are various more specific goals any production control team wants to accomplish:
- Meeting deadlines
- Ensuring high product quality and minimizing rejects
- Optimal machine allocation
- Optimal use of materials
- Eliminating risks to worker safety and health
- … and many more
Thankfully, digitalization and technological development has provided production control teams with various software solutions that help fulfill the goals mentioned above. In the next section, we will take a closer look at these tools.
Tools
Important tools for production control
In order to organize and fulfill the complex tasks associated with production control, many companies rely on a suite of specialized (software) tools. Today, manufacturers are able to choose between a vast amount of possible approaches and solutions – yet most of them share common characteristics and features.
The following categorization classifies tools based on their concrete area of application within production control – or more specifically, the task they try to support.
Scheduling software: These applications help create complex schedules, visualize resource allocation, and track progress.
Monitoring tools: These systems collect and visualize machine-data in real-time and thus provide insights into production performance. Ideally, they also provide options for manual interaction.
Reporting tools: Common reporting tools allow for the creation of dashboards and reports summarizing output, efficiency, and problem areas, supporting continuous improvement efforts.
Communication tools: Production control is a critical aspect for the success of a manufacturer – but not the only one. Effective communication, not only within the production control team but also with other departments like sales and procurement, is essential to daily operations.
Many software applications combine multiple of the functions mentioned above. Additionally, technologies and concepts such as cloud computing, edge computing or no-code development are increasingly being utilized in manufacturing solutions.
Our innovative manubes platform is an example of a large-scale, cloud-based solution tailored to industrial production management. manubes allows users to collect and structure production data, create highly customizable real-time visualizations and reports and manage various production processes using automated workflows.

Digital production management in the cloud
With manubes, you are able to systematically automate production processes and visualize all areas of a production in real time.
The manubes platform offers worldwide access via web browser, easy operation and maximum security for production data.
Discover manubes!
Cloud-based production management with manubes: Our innovative platform offers specialized tools for connecting production systems, managing and visualizing production data and automating production processes. manubes users benefit from a powerful infrastructure, worldwide access and maximum security.