Basics & Examples
Workflow Automation in Manufacturing
By automating manual work steps, manufacturing companies can save time and costs, reduce errors and ensure consistent processes. We show examples of possible workflow automations in production.
Workflow automation refers to the combination of individual actions or work steps into a sequence (workflow) that is automated and executed in a specific order.
The execution of a workflow is based on predefined rules. These include trigger conditions that activate the workflow under certain circumstances or branches that check specific attributes and then follow different paths accordingly.
Workflow automation offers many advantages:
- Cost and time savings through the automation of manual tasks
- Lower error rates by avoiding manual data entry
- Consistent processes through predefined rules
- Improved traceability and troubleshooting
- Often flexible customization options
To design and implement custom workflows, companies often utilize workflow software. These typically come with prebuilt action blocks that can be combined into workflows through a graphical user interface.
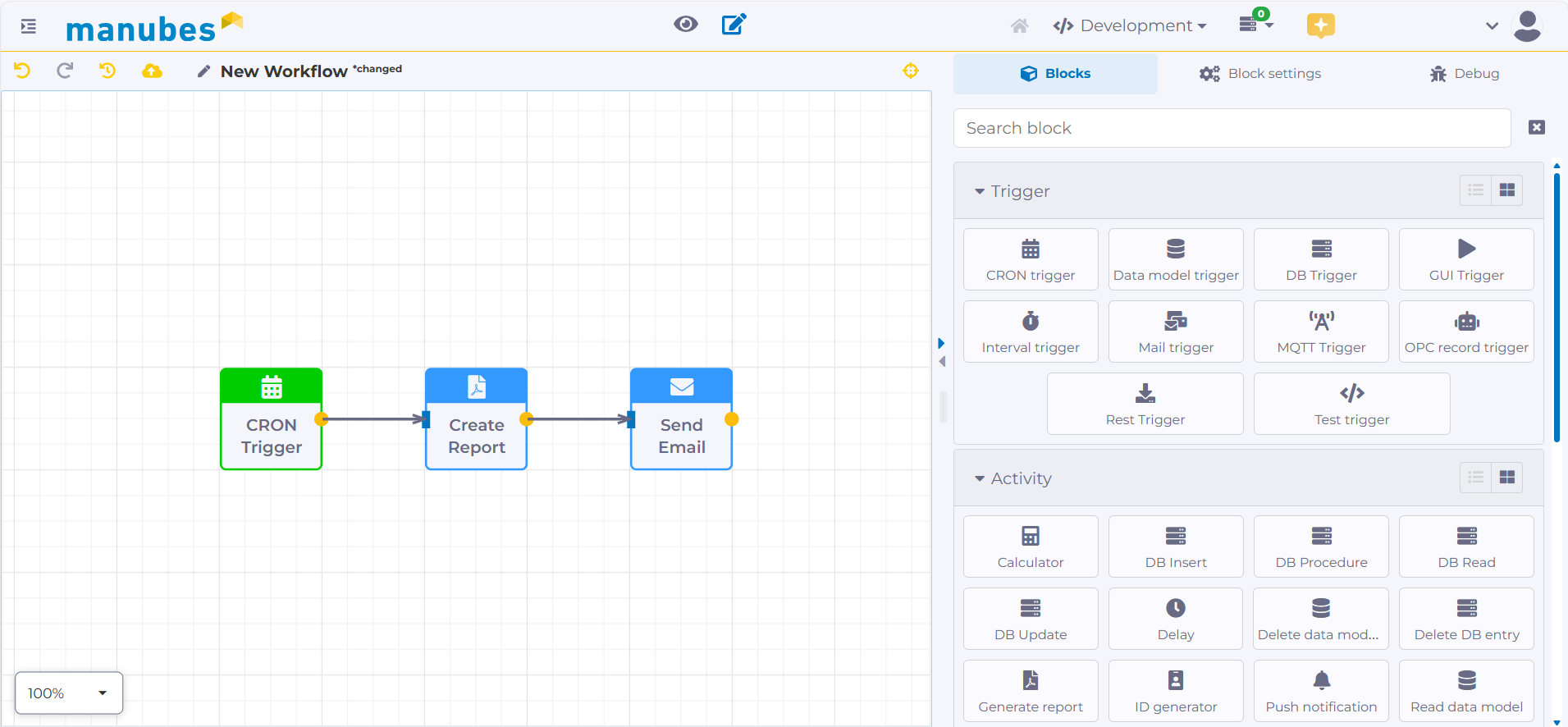
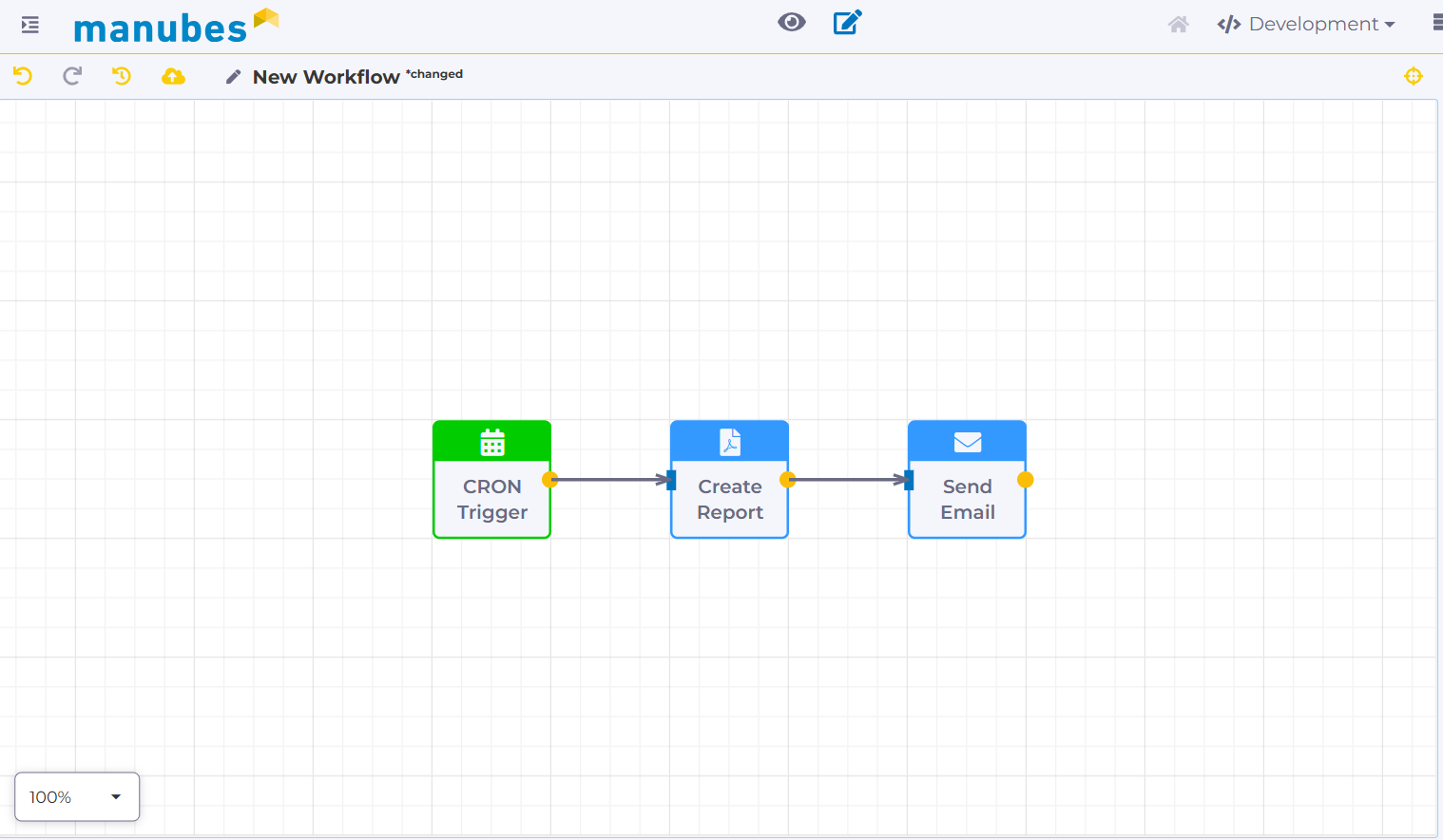
The manubes Workflow Designer – specialized for industrial production
Workflow Automation in Manufacturing: Opportunities and Challenges
Similarly to industries like financial services, insurance and public administration, industrial production can also benefit significantly from workflow automation.
Opportunities exist in pretty much all areas: From the complex field of production planning, production control and production monitoring to specific tasks related to equipment maintenance, personnel management, documentation or reporting.
One of the biggest challenges lies in integrating workflow software with existing systems. While in many other industries primarily administrative processes at the enterprise level are automated, manufacturing also involves systems in close proximity to the production processes such as MES and SCADA, along with the machines and devices present on the shop floor.
When workflows interact with machine parameters, these must therefore be available in real time. This requires support for appropriate interfaces such as OPC UA or REST API client functionality within the workflow tools.
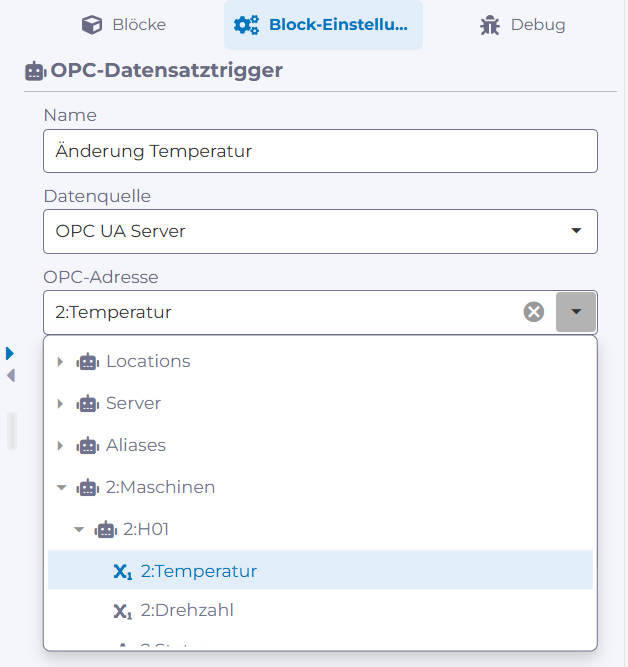
Zugriff auf OPC UA-Datenpunkte im manubes Workflow Designer
Another crucial aspect is the ability to quickly make changes to or scale existing workflows.. This is especially true in production, where conditions frequently change, and processes need to be adjusted. Many workflow solutions rely entirely on no-code, enabling the creation and modification of workflows through simple dialogs or drag-and-drop functionality.
Features such as version control, staging, diagnostics and monitoring simplify the management of workflow automations and provide greater transparency and security.
Finally, workflows also generate data (e.g. the number of successful executions), which is relevant for analyses, optimizations, or meeting compliance requirements.
Examples
Workflow Automation in Manufacturing: 3 Examples
The following section introduces three use cases for workflow automations in industrial production:
Notifications & Alarming
A classic use case for workflows is sending automated notifications in response to specified events.
In production, they could be used to:
- Immediately notify responsible personnel in the event of disruptions
- Inform maintenance teams when servicing is required
- Keep production managers updated on order progress
- Display warnings about material shortages, high energy consumption or quality issues
Notifications can be implemented via email, push notification or through integration with messenger services or platforms such as Microsoft Teams.
Possible triggers include changes in process parameters, machine status, energy consumption or inventory levels. Manual triggering via a button or similar action is also possible.
With manubes, workflows not only have access to all data in existing data models (provided you have the appropriate access rights), but also to live data from machine and system integrations. This allows value changes to be set as triggers for notification workflows with just a few clicks.
Thanks to its flexible Workflow Designer and extensive integration capabilities, manubes is suitable both for custom real-time notifications and for comprehensive alarm management solutions.
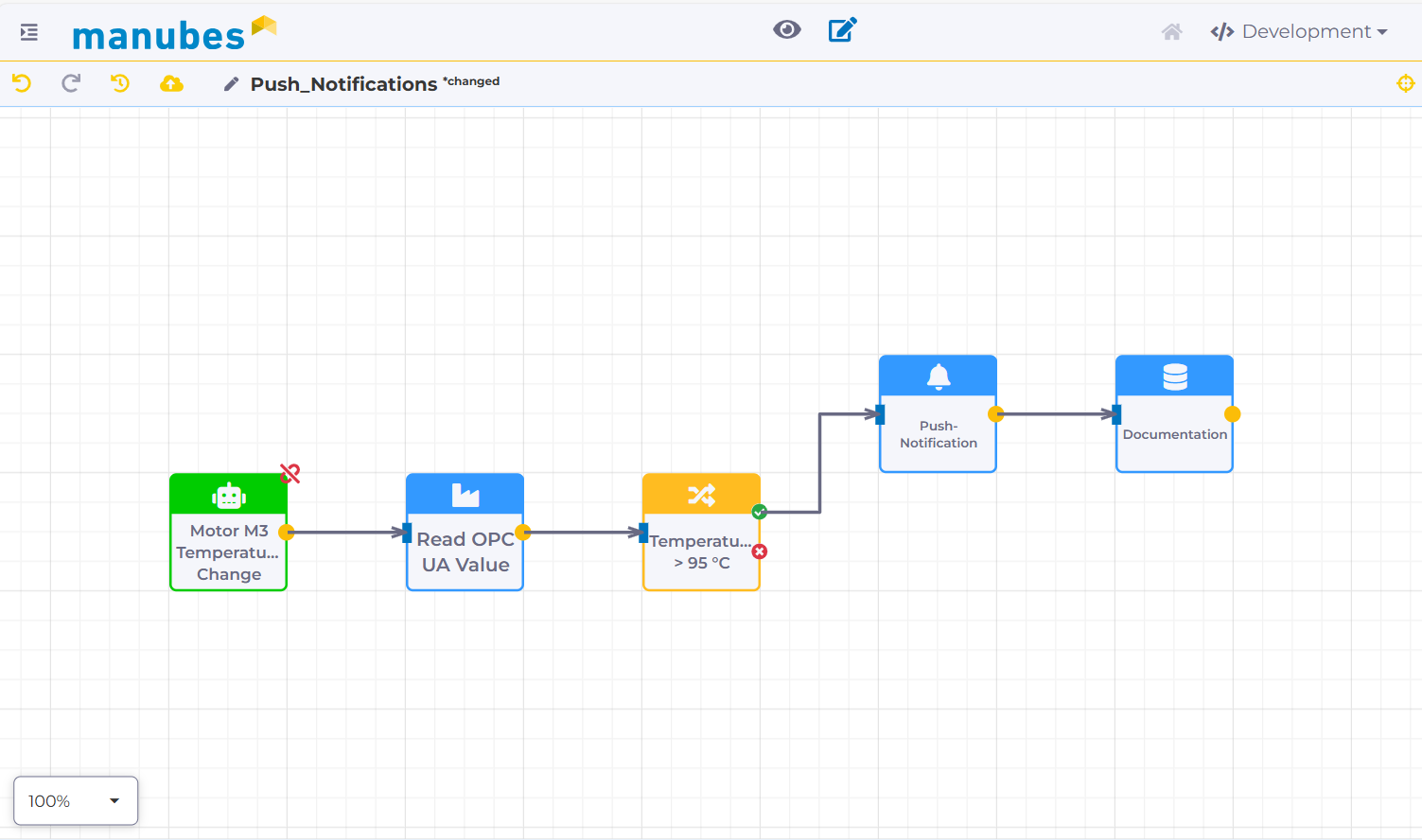
Workflow example 1: Sending a push notification when a specified temperature value is exceeded
Automated Reporting
The creation and distribution of production reports has traditionally been time-consuming – especially the process of collecting and consolidating data from different systems, which takes a lot of effort when done manually.
With manubes, you can automate large parts of production reporting using workflows.
Creating a new report in PDF format can be set up as a simple workflow step. To do this, create your own report template and link it to real-time data sources such as your data models, external databases, or OPC UA servers in production.
This ensures that your report is always based on the most up-to-date data at the time of creation.
The workflow can be triggered either by a time-based event or a user action (e.g. clicking a button). As a result, you can not only distribute reports to selected recipients at regular intervals but also make them available on demand as part of reporting portals or dashboards.
By automating report creation and distribution through workflows, you not only achieve significant time savings but also ensure transparency regarding production metrics, progress and developments – always based on the latest data.
Workflow example 2: Automated creation and distribution of production reports
Integration of AI systems
The integration of artificial intelligence in production can also be simplified with the right workflow tools, e.g. by passing production data to AI models for analysis and then processing the results.
Depending on the use case, these may be local, self-trained models or external APIs.
Possible applications include quality inspections using image recognition systems, anomaly detection or the preparation of raw data in the form of reports.
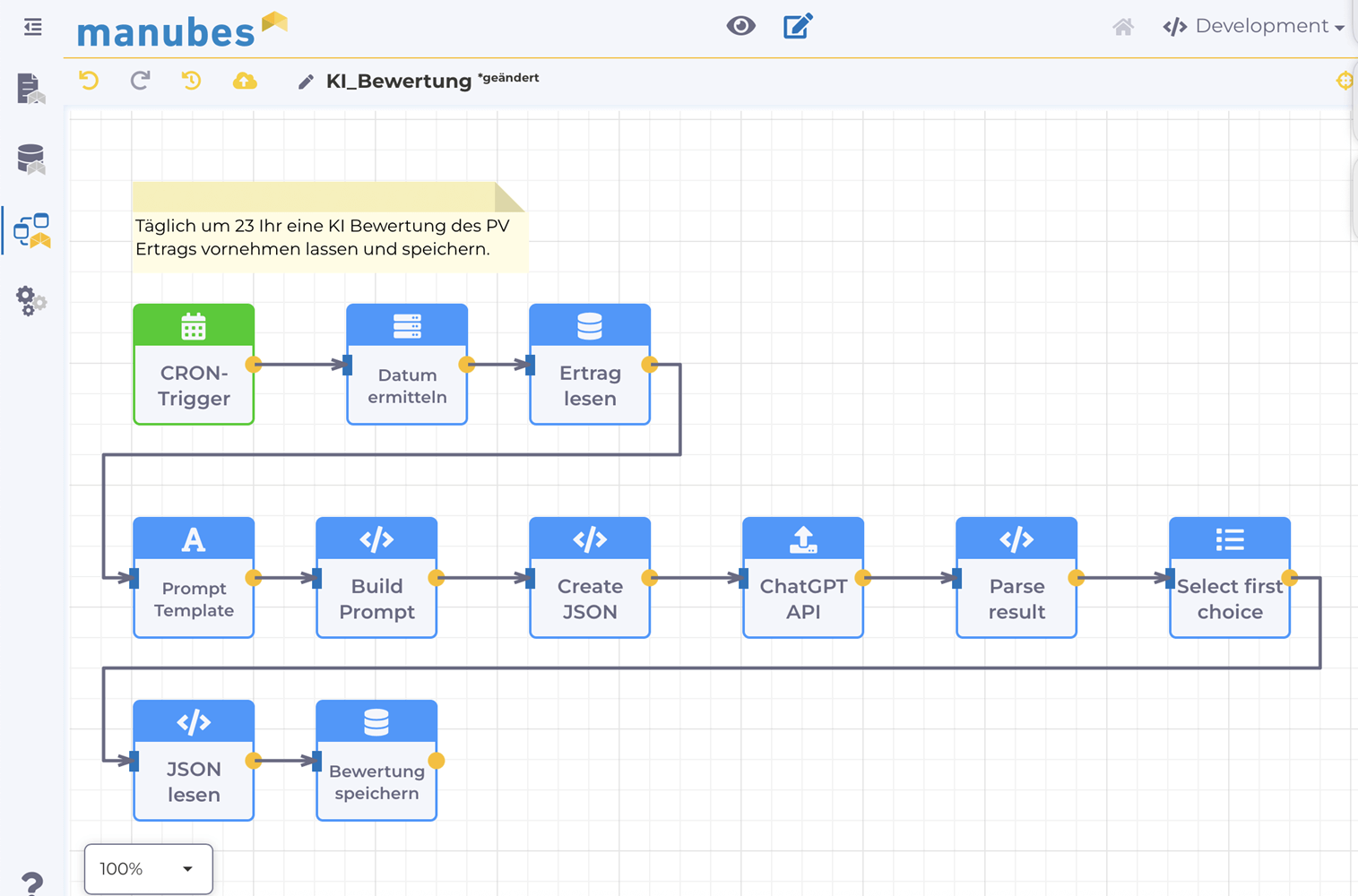
Workflow example 3: Passing asset performance data to the OpenAI API for evaluation
manubes as a Workflow Solution
Increase your production efficiency through workflow automation
manubes is an innovative digitalization solution that combines a wide range of tools for production optimization in a flexible cloud platform. Manufacturers are able to collect, store and visualize production data from many different sources, using standardized interfaces such as OPC UA or MQTT.
In the background, the manubes Workflow Designer enables fine-grained control and automation of production-related processes and reocurring tasks. Create your own automations via drag-and-drop and include data sources and systems, whether on the shopfloor or on the enterprise level.
The result are powerful solutions tailored precisely to your production environment: From comprehensive dashboards with integrated control options to order release and material procurement.
Which processes are you looking to automate?
Get in touch with the manubes team – we will be happy to discuss your specific requirements.
Try manubes for free
Test the different manubes features in your personal cloud environment.
